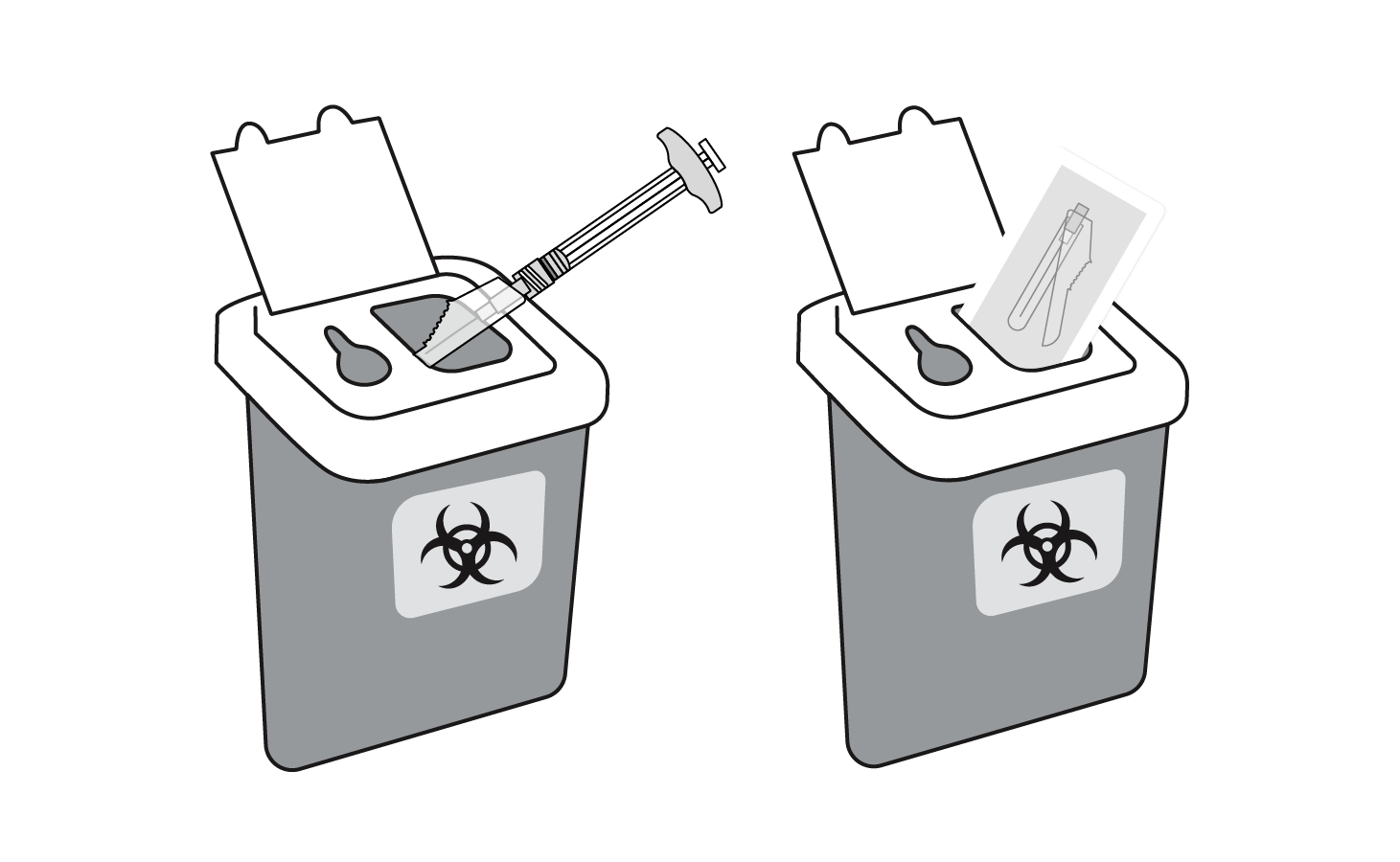
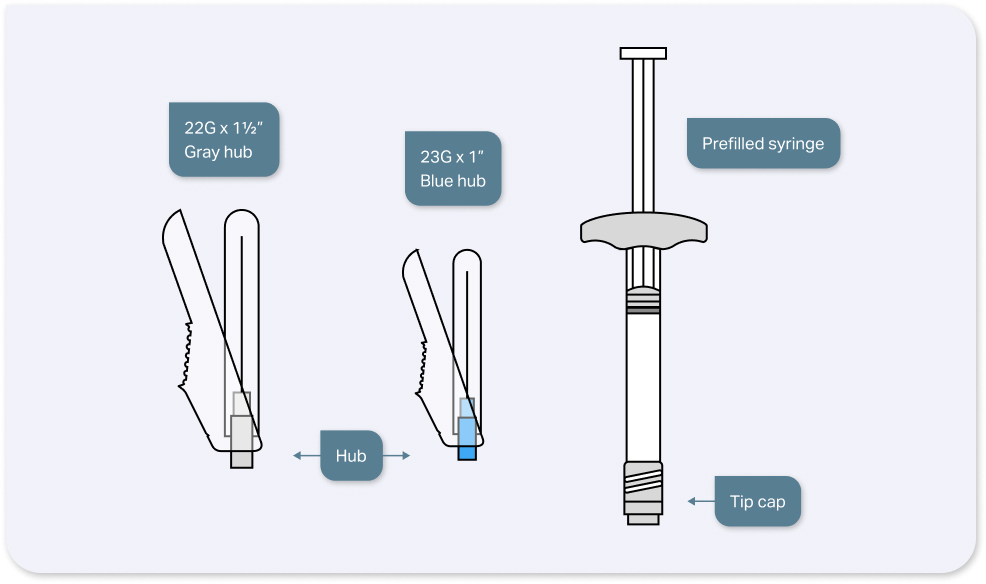
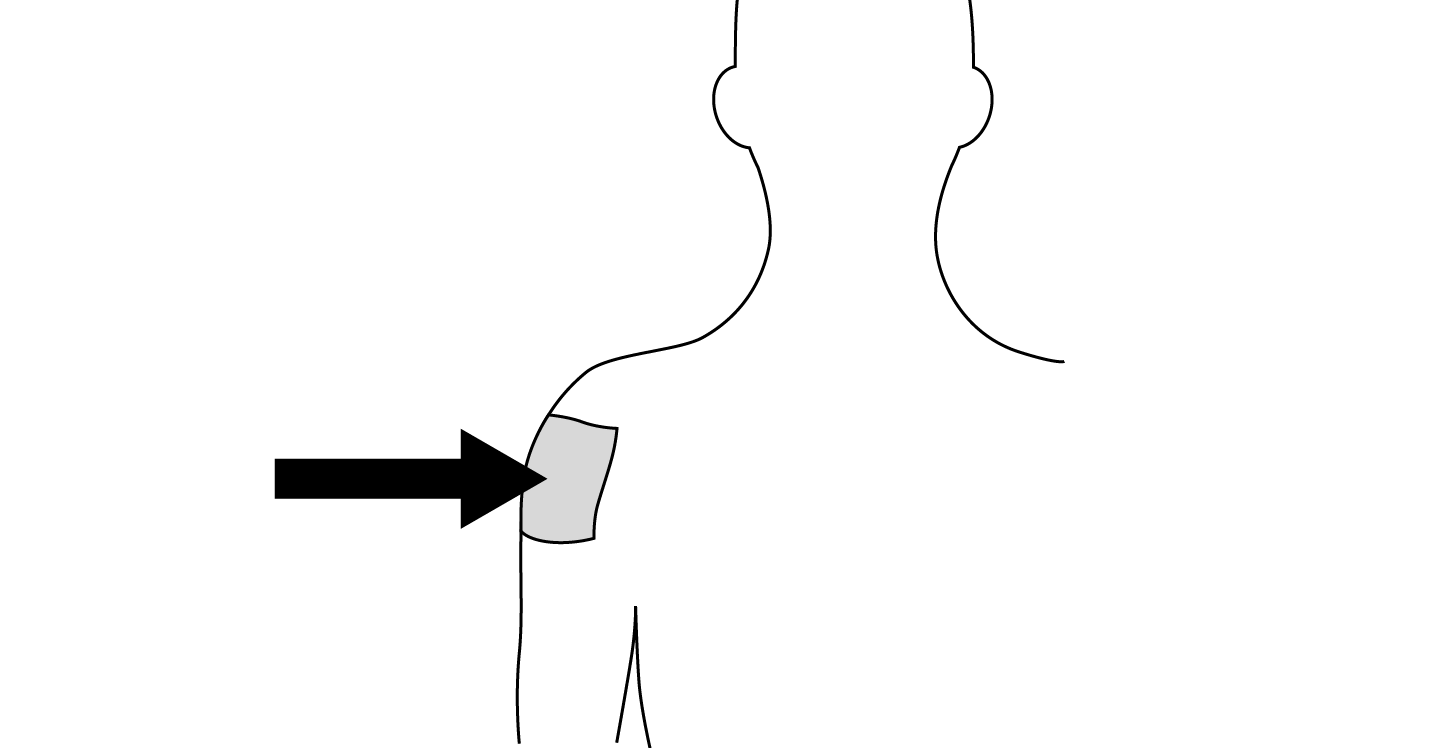
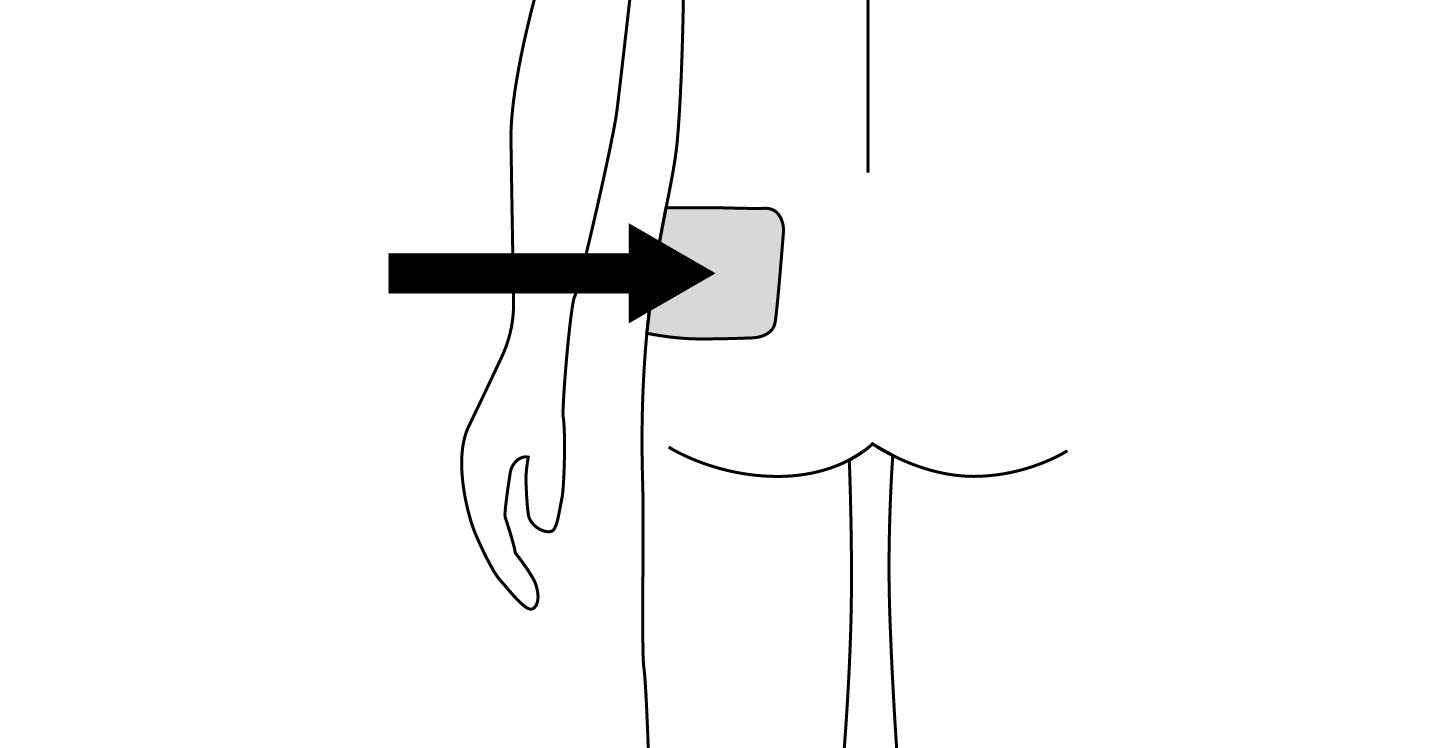
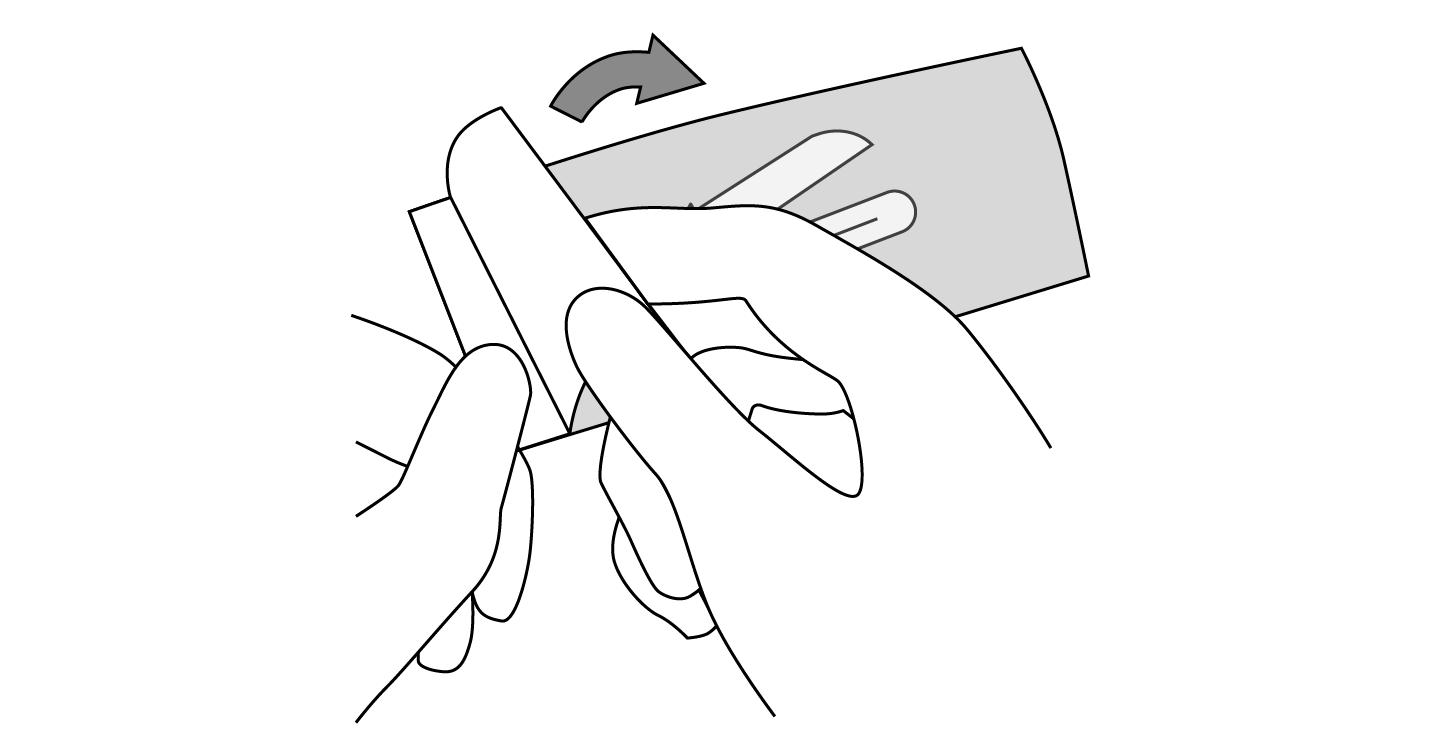
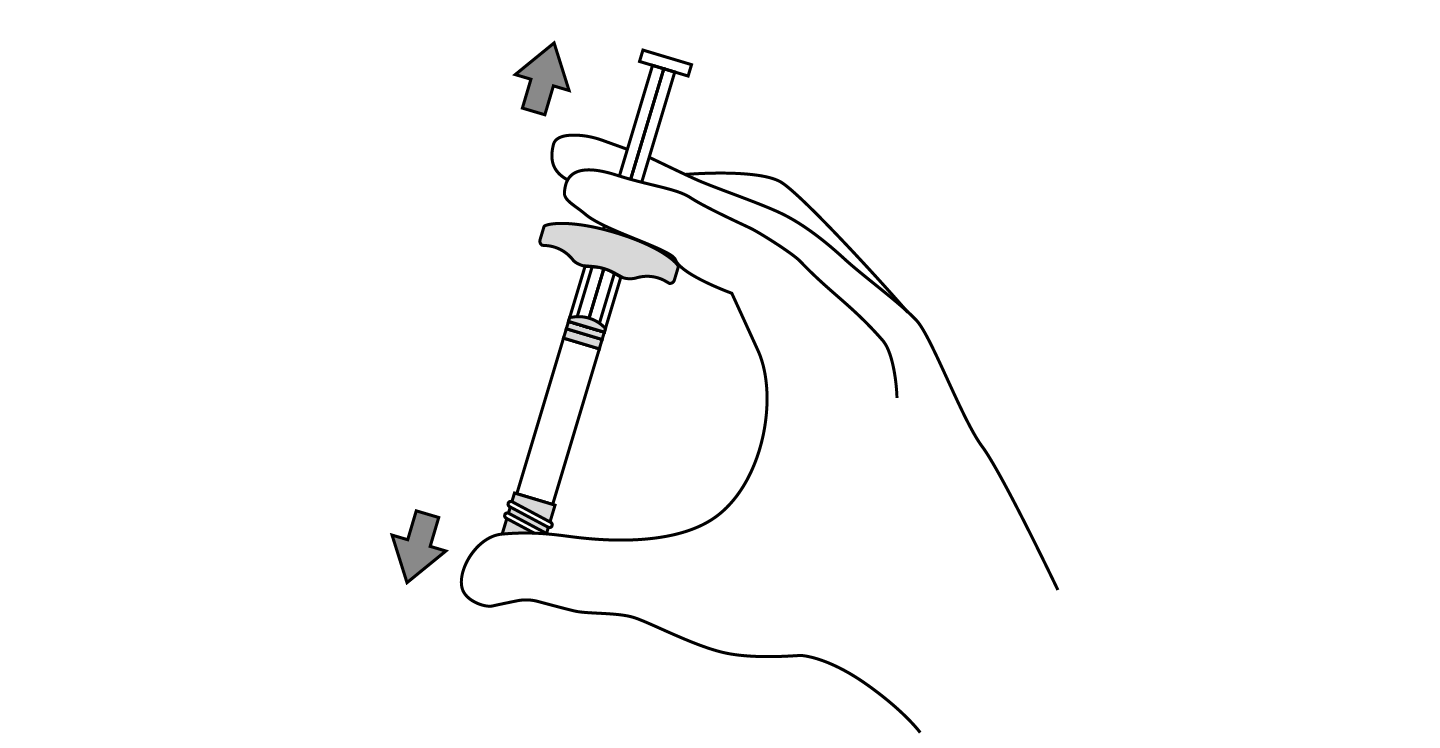
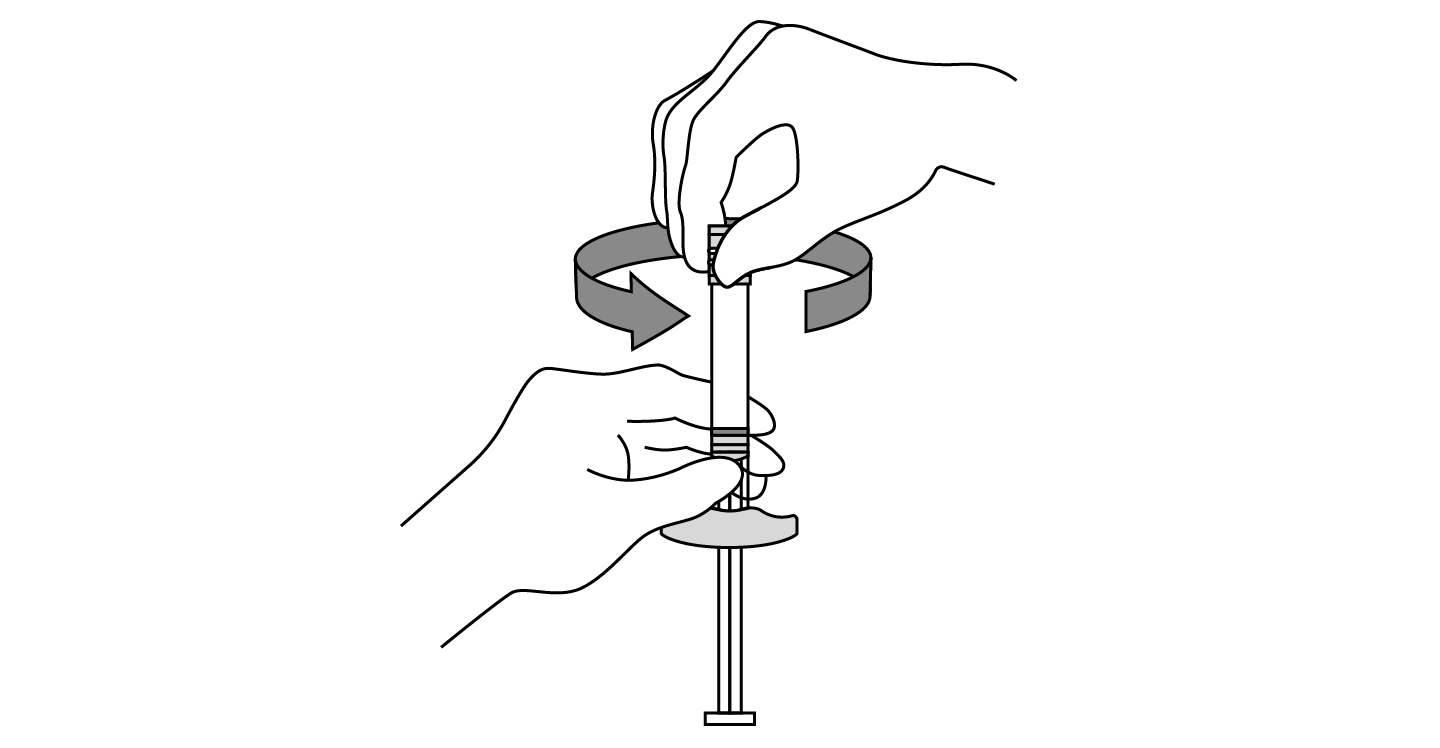
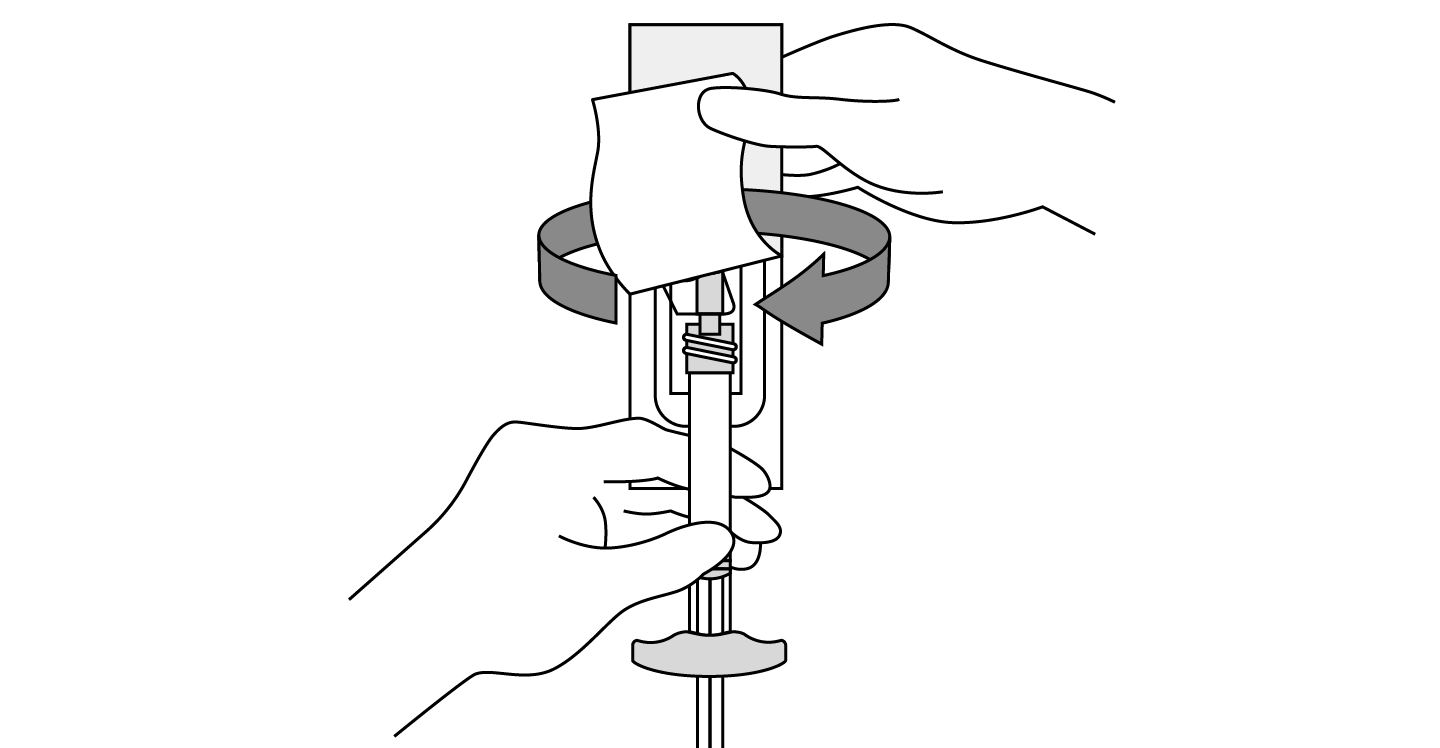
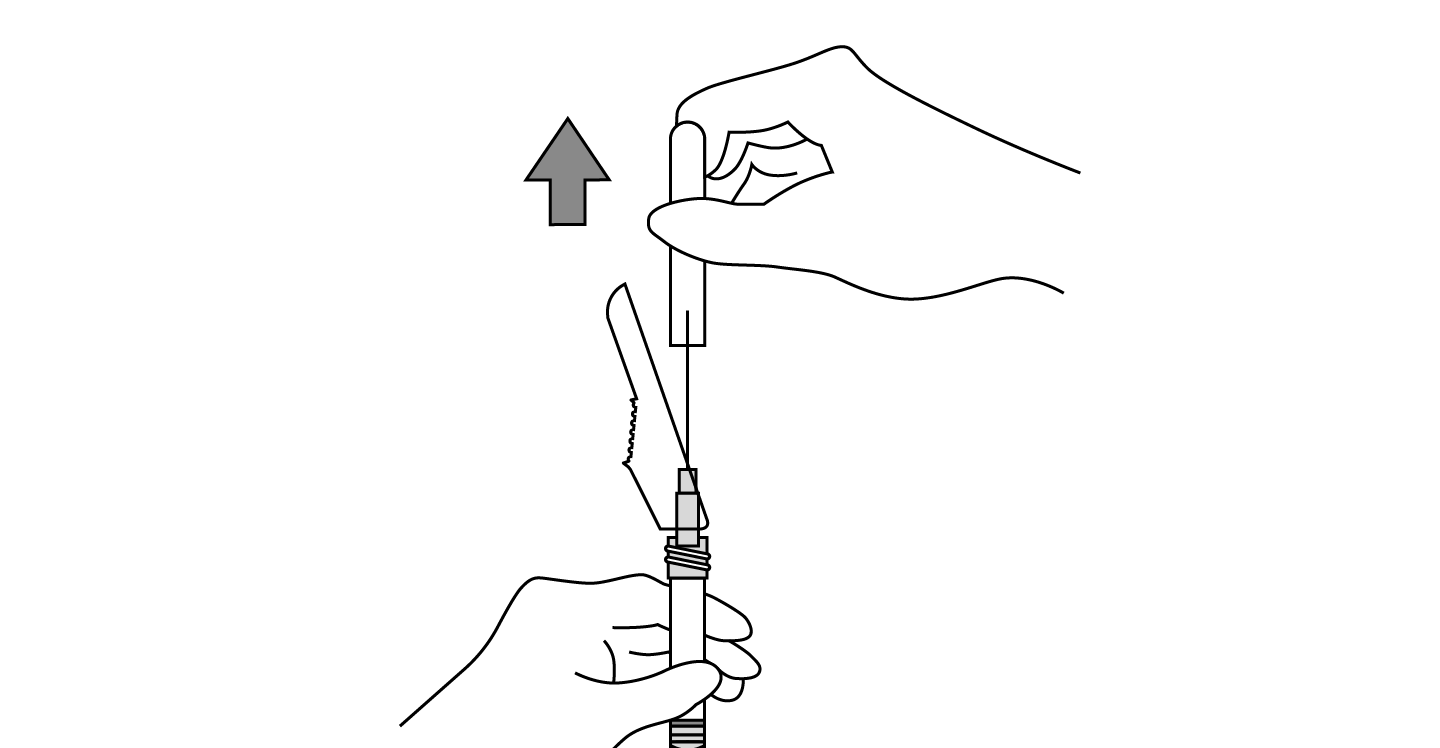
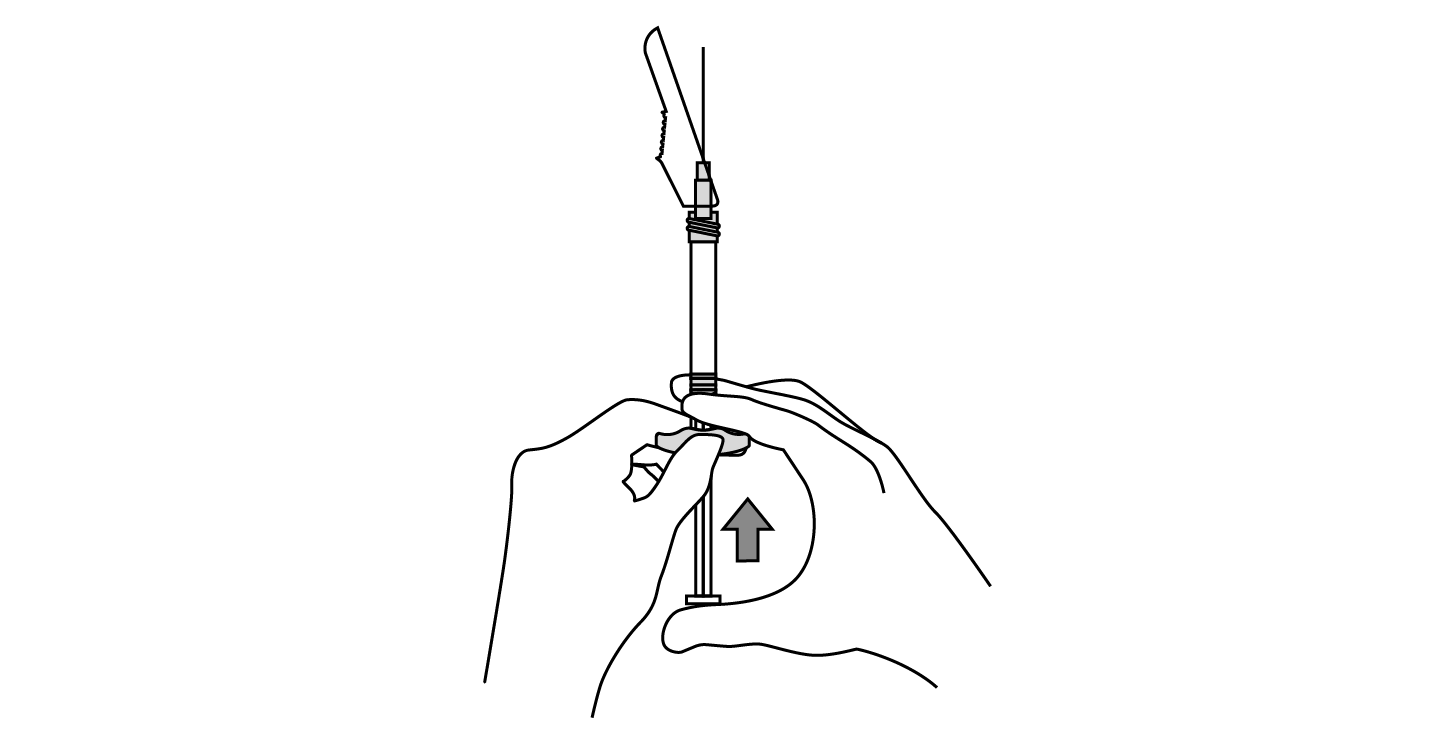
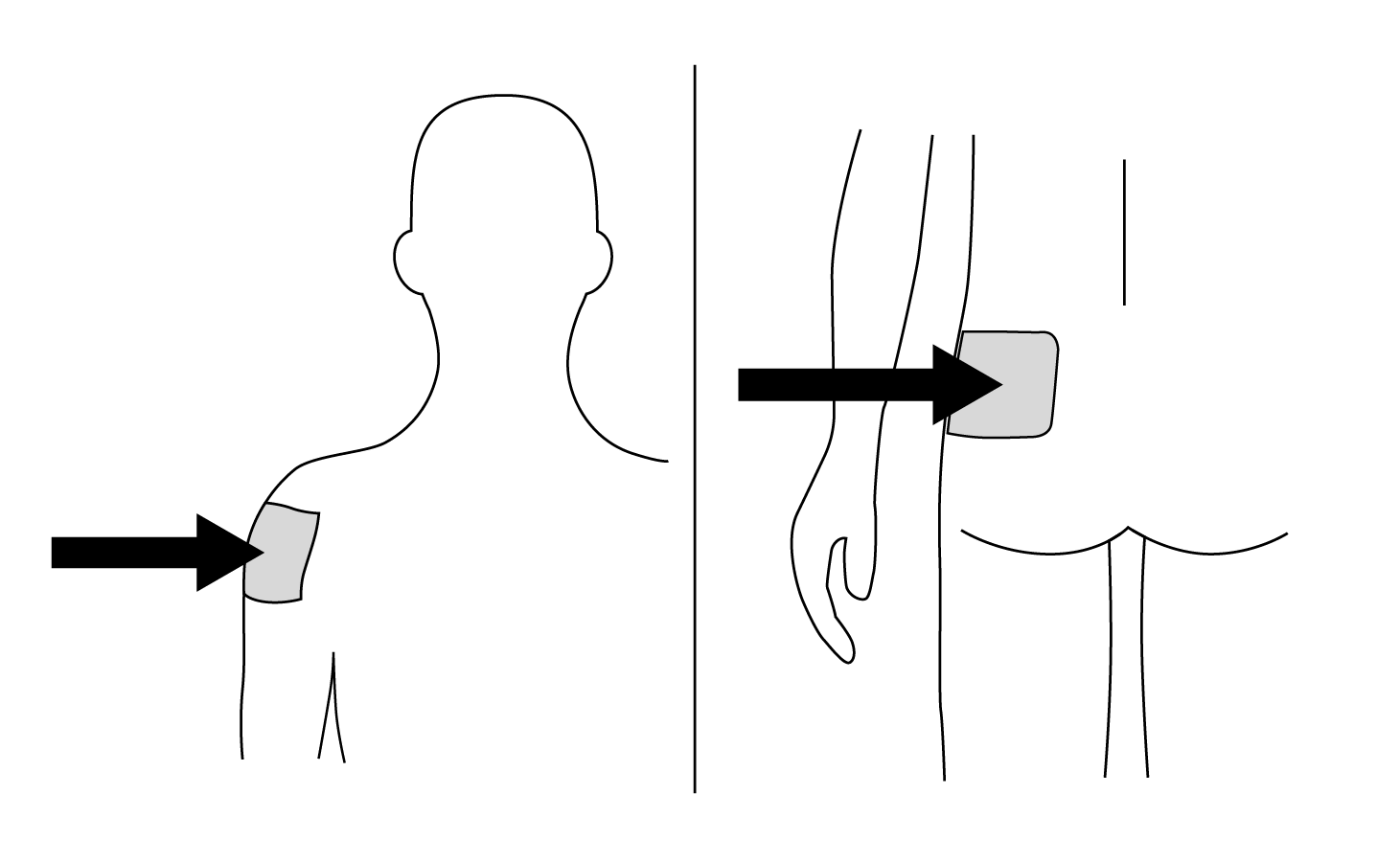
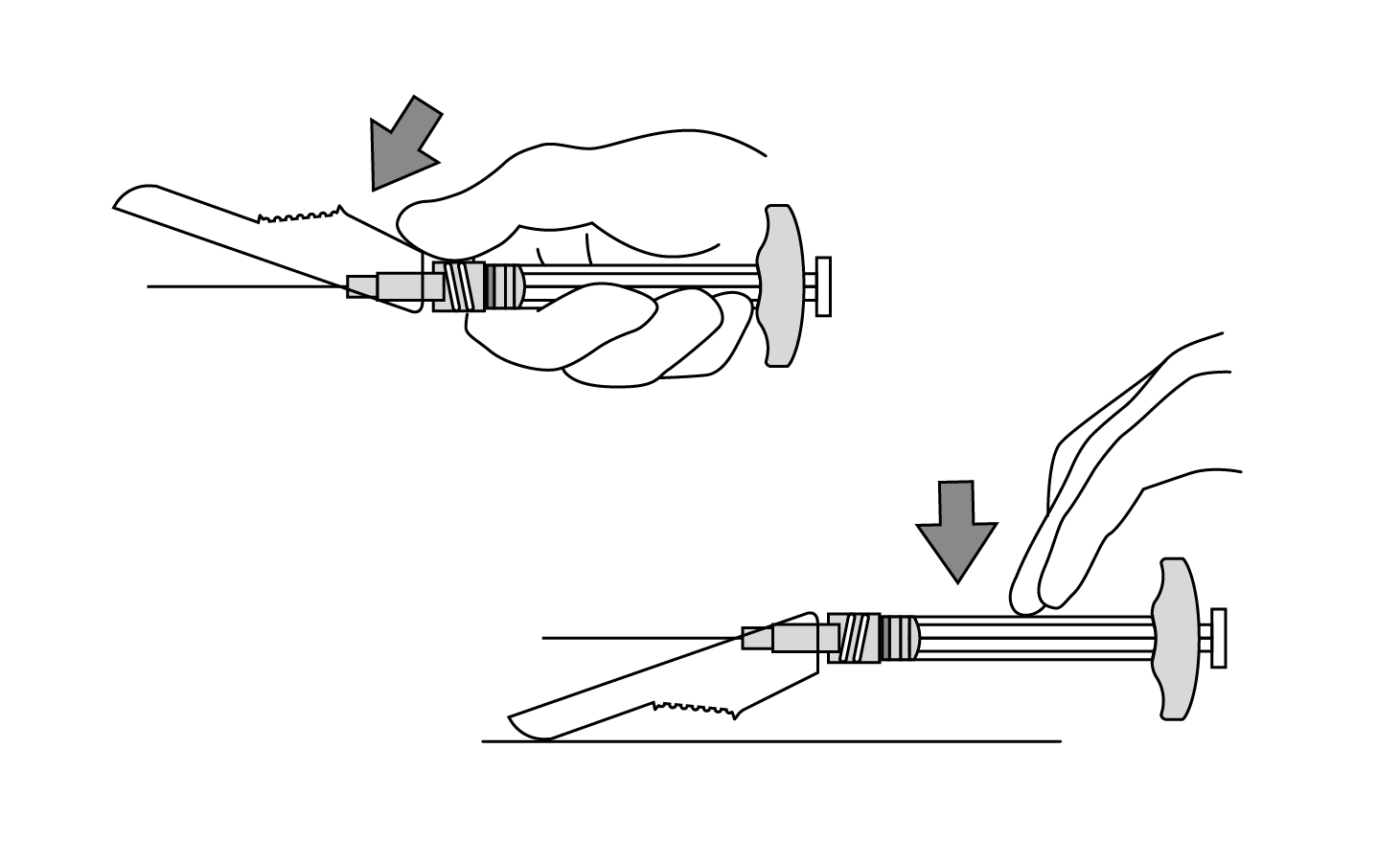
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE: ERZOFRI® (paliperidone palmitate) extended-release injectable suspension for intramuscular use is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for the treatment of:
- schizophrenia in adults
- schizoaffective disorder in adults as monotherapy and as an adjunct to mood stabilizers or antidepressants
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR ERZOFRI
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. ERZOFRI is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ERZOFRI is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to paliperidone, risperidone, or to any excipients in ERZOFRI.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis: Increased incidence of cerebrovascular adverse reactions (e.g., stroke, transient ischemic attacks) including fatalities.
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): NMS, a potentially fatal symptom complex, has been reported in association with antipsychotic drugs. Manage with immediate discontinuation and close monitoring.
- QT Prolongation: Avoid use with drugs that also increase QT interval and in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval and patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
- Tardive Dyskinesia (TD): TD, a syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements, may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. ERZOFRI should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize occurrence of TD. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients: (1) who suffer from a chronic illness that is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs and (2) for whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who require chronic treatment, use the lowest dose and shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response. Periodically reassess the need for continued treatment.
If signs and symptoms of TD appear in a patient treated with ERZOFRI, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment with ERZOFRI despite the presence of the syndrome.
- Metabolic Changes: Atypical antipsychotic drugs have caused metabolic changes, including hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and body weight gain that may increase the cardiovascular/cerebrovascular risk.
- Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus: Monitor for hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and weight gain. Patients with an established diagnosis of diabetes mellitus who are started on atypical antipsychotics should be monitored regularly for worsening glucose control. Patients with risk factors for diabetes mellitus (e.g., obesity, family history of diabetes) who are starting treatment with atypical antipsychotics should undergo fasting blood glucose testing at the beginning of treatment and periodically during treatment. Any patient treated with atypical antipsychotics should be monitored for symptoms of hyperglycemia including polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, and weakness. Patients who develop symptoms of hyperglycemia during treatment with atypical antipsychotics should undergo fasting blood glucose testing. In some cases, hyperglycemia resolved when the atypical antipsychotic was discontinued; however, some patients required continuation of anti-diabetic treatment despite discontinuation of the suspect drug.
- Dyslipidemia: Undesirable alterations in lipids have been observed in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics.
- Weight Gain: Weight gain has been observed with atypical antipsychotic use. Clinical monitoring of weight is recommended.
- Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope: Paliperidone may induce orthostatic hypotension and syncope in some patients because of its alpha-adrenergic blocking activity. Use ERZOFRI with caution in patients with known cardiovascular disease (e.g., heart failure, history of myocardial infarction or ischemia, conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease, or conditions that predispose the patient to hypotension (e.g., dehydration, hypovolemia, and treatment with antihypertensive medications). Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in patients who are vulnerable to hypotension.
- Falls: Somnolence, postural hypotension, motor and sensory instability have been reported with the use of antipsychotics, including paliperidone palmitate, which may lead to falls, and consequently, fractures or other fall-related injuries.
- Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: In clinical trial and/or postmarketing experience, events of leukopenia and neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents, including once-a-month paliperidone palmitate. Agranulocytosis has also been reported. Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC)/absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia. In patients with a history of a clinically significant low WBC/ANC or a drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia, perform a complete blood count (CBC) frequently during the first few months of therapy. In such patients, consider discontinuation of ERZOFRI at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors. Monitor patients with clinically significant neutropenia for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treat promptly if such symptoms or signs occur. Discontinue ERZOFRI in patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count <1000/mm3) and follow their WBC until recovery.
- Hyperprolactinemia: Paliperidone elevates prolactin levels and the elevation persists during chronic administration. Paliperidone has a prolactin-elevating effect similar to that seen with risperidone, a drug that is associated with higher levels of prolactin than other antipsychotic drugs. Long-standing hyperprolactinemia, when associated with hypogonadism may lead to decreased bone density in both female and male subjects.
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Somnolence, sedation, and dizziness were reported as adverse reactions in subjects treated with another once-a-month paliperidone palmitate extended-release injectable suspension. Antipsychotics, including ERZOFRI, have the potential to impair judgement, thinking, or motor skills. Patients should be cautioned about performing activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating hazardous machinery or operating a motor vehicle, until they are reasonably certain that paliperidone therapy does not adversely affect them.
- Seizures: Like other antipsychotic drugs, ERZOFRI should be used cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or other conditions that potentially lower the seizure threshold.
- Dysphagia: Esophageal dysmotility and aspiration have been associated with antipsychotic drug use. ERZOFRI and other antipsychotic drugs should be used cautiously in patients at risk for aspiration.
- Priapism: Drugs with alpha-adrenergic blocking effects have been reported to induce priapism.
- Disruption of Body Temperature Regulation: Disruption of the body’s ability to reduce core body temperature has been attributed to antipsychotic agents. Appropriate care is advised when prescribing ERZOFRI to patients who will be experiencing conditions which may contribute to an elevation in core body temperature, e.g. exercising strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving concomitant medication with anticholinergic activity, or being subject to dehydration.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and occurring at least twice as often as placebo) were injection site reactions, somnolence/sedation, dizziness, akathisia, and extrapyramidal disorder.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy Exposure Registry: There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to atypical antipsychotics, including ERZOFRI, during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by contacting the National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics at 1-866-961-2388 or online at http://womensmentalhealth.org/clinicaland-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/.
Risk Summary: Neonates exposed to antipsychotic drugs during the third trimester of pregnancy are at risk for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms following delivery. Overall, available data from published epidemiologic studies of pregnant women exposed to paliperidone have not established a drug-associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother associated with untreated schizophrenia and with exposure to antipsychotics, including ERZOFRI, during pregnancy.
Lactation: Infants exposed to ERZOFRI through breastmilk should be monitored for excess sedation, failure to thrive, jitteriness, and extrapyramidal symptoms (tremors and abnormal muscle movements).
Fertility: Treatment with ERZOFRI may result in an increase in serum prolactin levels, which may lead to a reversible reduction in fertility in females of reproductive potential.
Renal Impairment: Use of ERZOFRI is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min).
Patients with Parkinson’s Disease or Lewy Body Dementia: Patients with Parkinson’s Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies can experience increased sensitivity to ERZOFRI. Manifestations can include confusion, obtundation, postural instability with frequent falls, extrapyramidal symptoms, and clinical features consistent with neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Please see full Prescribing Information for ERZOFRI® including BOXED WARNING.
References: 1. ERZOFRI® [Prescribing Information]. Princeton, NJ: Luye Pharma Group Ltd. 2. Dong Y, Glass S, Sonnenberg JG, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of LY03010, a novel monthly intramuscular injectable extended-release paliperidone palmitate suspension in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Poster presented at: Psych Congress Elevate; May 30-June 2, 2024; Las Vegas, NV. 3. Hough D, Gopal S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Morozova M, Eerdekens M. Paliperidone palmitate maintenance treatment in delaying the time-to-relapse in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2010;116(2-3):107-117. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2009.10.026 4. Fu DJ, Turkoz I, Simonson RB, et al. Paliperidone palmitate once-monthly reduces risk of relapse of psychotic, depressive, and manic symptoms and maintains functioning in a double-blind, randomized study of schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(3):253-262. doi:10.4088/JCP.14m09416
Reference: 1. ERZOFRI® [Prescribing Information]. Princeton, NJ: Luye Pharma Group Ltd.
Reference: 1. Dong Y, Glass S, Sonnenberg JG, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of LY03010, a novel monthly intramuscular injectable extended-release paliperidone palmitate suspension in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Poster presented at: Psych Congress Elevate; May 30-June 2, 2024; Las Vegas, NV. 2. ERZOFRI® [Prescribing Information]. Princeton, NJ: Luye Pharma Group Ltd.
References: 1. ERZOFRI® [Prescribing Information]. Princeton, NJ: Luye Pharma Group Ltd. 2. Hough D, Gopal S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Morozova M, Eerdekens M. Paliperidone palmitate maintenance treatment in delaying the time-to-relapse in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2010;116(2-3):107-117. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2009.10.026
References: 1. ERZOFRI® [Prescribing Information]. Princeton, NJ: Luye Pharma Group Ltd. 2. Fu DJ, Turkoz I, Simonson RB, et al. Paliperidone palmitate once-monthly reduces risk of relapse of psychotic, depressive, and manic symptoms and maintains functioning in a double-blind, randomized study of schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(3):253-262. doi:10.4088/JCP.14m09416
References: 1. ERZOFRI® [Prescribing Information]. Princeton, NJ: Luye Pharma Group Ltd. 2. Russu A, Kern Sliwa J, Ravenstijn P, et al. Maintenance dose conversion between oral risperidone and paliperidone palmitate 1 month: Practical guidance based on pharmacokinetic simulations. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72(6):e13089. doi:10.1111/ijcp.13089